Alternative Approaches to Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment
Alternative Approaches to Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment
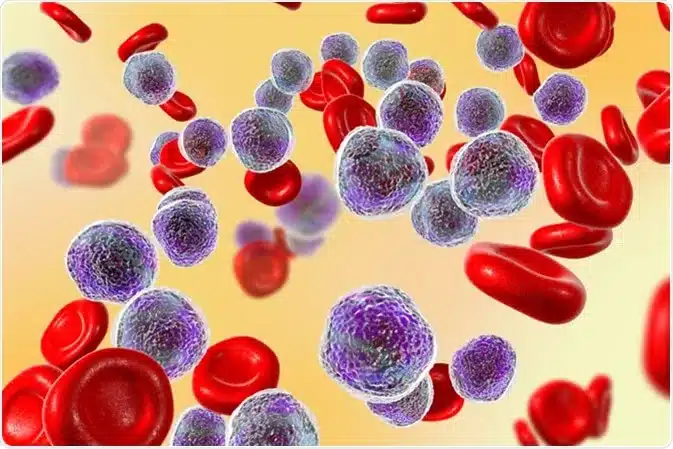
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL) is a type of cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It develops when the body produces too many immature white blood cells, called lymphocytes. Normally, white blood cells help the body fight infection. In ALL, too many immature lymphocytes are made in the bone marrow and spill into the bloodstream. These “blast” cells are unable to fight infection as well as healthy white blood cells can, making people with ALL more vulnerable to infections and other complications.
This type of cancer typically progresses quickly so treatment should be started right away. The goal of treatment is to kill all leukemia cells or put them into remission for long-term survival or cure for some patients with ALL. Treatment plans for acute lymphocytic leukemia treatment may include chemotherapy (drugs that kill cancerous cells), radiation therapy (high-energy X-rays used to kill cancerous cells), stem cell transplantation (transplanting healthy stem cells from the donor’s or patient’s own body back into the patient’s bloodstream), and/or targeted therapy drugs that target specific molecules involved in tumor growth and spread).
Treatment
Acute lymphocytic leukemia treatment varies depending on the individual and the type of disorder they’re facing. Whether you’re dealing with depression, anxiety, or addiction, there are a variety of treatments available that can help you manage your condition and ultimately lead to a healthier life. Let’s take a look at some of the most common types of treatment available for mental health issues.
1) Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy is one of the most popular forms of treatment for mental illness. It involves talking with a qualified therapist about your thoughts and feelings to gain insight into your behaviour and find ways to better manage it. Therapists may use cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), or other techniques depending on their clients’ needs. These therapies can help people understand how their thoughts affect their behaviours and learn ways to modify them to improve their emotional well-being over time.
2) Medication: Another common form of treatment is medication management which involves taking prescription drugs to treat symptoms associated with certain disorders such as depression or anxiety. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly
Chemotherapy: Side Effects and Benefits
Chemotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can be taken orally, injected into a vein, or applied directly to the skin. The side effects and benefits of chemotherapy vary from patient to patient, but it is important for people undergoing chemotherapy to be aware of both.
One of the most common side effects associated with chemotherapy is fatigue. This tiredness can last for days or weeks after treatment and can make it difficult for patients to perform everyday tasks. Other common side effects include nausea, vomiting, hair loss and an increased risk of infection due to a weakened immune system. Some patients may also experience changes in their sense of taste or smell, as well as other physical discomforts such as mouth sores and constipation.
The main benefit of chemotherapy is that it can help treat cancer by destroying tumor cells or slowing their growth rate. In some cases, chemotherapy has even been known to cure certain types of cancers completely. Chemotherapy also helps reduce pain and other symptoms associated with cancer by shrinking tumors and reducing pressure on organs or nerves caused by the tumor’s growth rate.
Therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that utilizes drugs or other substances to directly target the proteins, genes, or tissue environment involved in cancer cell growth and survival. This type of therapy has been used with more success than traditional chemotherapy in many types of cancer and is becoming increasingly popular as an alternative to traditional treatments.
The primary benefit associated with targeted therapies is the ability of the drugs to specifically target cancer cells without harming healthy cells or tissues. This makes them much less toxic than traditional chemotherapy, which works by attacking all rapidly dividing cells regardless of whether they are healthy or not.
Stem Cell Transplants: Side Effects and Benefits
A stem cell transplant is a procedure in which stem cells from a donor’s bone marrow or blood are injected into the patient’s body, allowing for new and healthy cells to replace those damaged by illness or injury. While this treatment may offer significant benefits, it also carries certain risks and side effects.
One of the most common side effects associated with stem cell transplants is graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). In GVHD, the donor’s immune system begins attacking tissues of the recipient’s body, causing inflammation and organ damage. This condition can be mild and temporary or severe enough to require hospitalization.
The benefits of stem cell transplants vary depending on the individual situation but they can often result in improved quality of life for those with chronic illnesses such as leukemia or other forms of cancer as well as genetic diseases like sickle cell anaemia.
Clinical Trials for Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is an aggressive form of cancer that affects the white blood cells of the immune system. It generally progresses rapidly, and treatment options are often limited. Clinical trials offer a potential avenue for those with ALL, as they can provide access to new treatments and therapies that have not been approved by regulatory agencies.
Clinical trials for ALL involve testing various experimental treatments on patients to evaluate their safety and effectiveness. In most cases, clinical trials involve testing drugs or other therapies on humans before they are approved for general use by regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The goal of these studies is to determine if a particular therapy is safe and effective in treating a specific medical condition.
Conclusion
Acute lymphocytic leukemia is a complex and challenging cancer to treat, but advances in chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies have greatly improved outcomes for patients. Treatment plans are tailored to each individual patient’s needs and may include a combination of chemotherapy drugs, radiation therapy, stem cell transplantation, or targeted therapies such as monoclonal antibodies. While there is still no cure for this type of cancer, these treatments can help control the symptoms and may help prolong life. With early diagnosis and prompt treatment following evidence-based guidelines, patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia can experience a good quality of life during their treatment journey.
Lucas Noah is a tech-savvy writer with a solid academic foundation, holding a Bachelor of Information Technology (BIT) degree. His expertise in the IT field has paved the way for a flourishing writing career, where he currently contributes to the online presence... Read more


